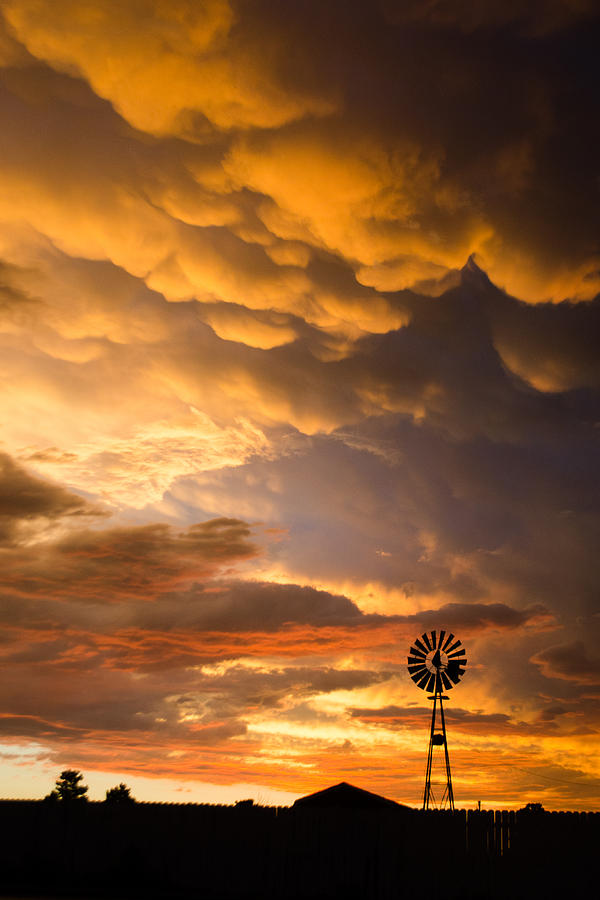
Stormy Sunrise

by Greni Graph
Title
Stormy Sunrise
Artist
Greni Graph
Medium
Photograph - Photography
Description
#201307191582-2 Sailboats and sailing ships have been using wind power for thousands of years, and architects have used wind-driven natural ventilation in buildings since similarly ancient times. The use of wind to provide mechanical power came somewhat later in antiquity. The windwheel of the Greek engineer Heron of Alexandria in the 1st century AD is the earliest known instance of using a wind-driven wheel to power a machine. The first windmills were in use in Iran at least by the 9th century and possibly as early as the 7th century. The use of windmills became widespread across the Middle East and Central Asia, and later spread to China and India. By 1000 AD, windmills were used to pump seawater for salt-making in China and Sicily. Windmills were used extensively in Northwestern Europe to grind flour from the 1180s, and windpumps were used to drain land for agriculture and for building.Early immigrants to the New World brought the technology with them from Europe. In the US, the development of the water-pumping windmill was the major factor in allowing the farming and ranching of vast areas otherwise devoid of readily accessible water. Windpumps contributed to the expansion of rail transport systems throughout the world, by pumping water from water wells for steam locomotives. The multi-bladed wind turbine atop a lattice tower made of wood or steel was for a century a fixture of the landscape throughout rural America. In 1881, Lord Kelvin proposed using wind power when coal ran out, as "so little of it is left". Solar power was also proposed, at about the same time. In July 1887, a Scottish academic, Professor James Blyth, built a cloth-sailed wind turbine in the garden of his holiday cottage in Marykirk and used the electricity it produced to charge accumulators which he used to power the lights in his cottage. His experiments culminated in a UK patent in 1891. In the winter of 1887/8 US inventor Charles F. Brush produced electricity using a wind powered generator which powered his home and laboratory until about 1900. In the 1890s, the Danish scientist and inventor Poul la Cour constructed wind turbines to generate electricity, which was used to produce hydrogen and Oxygen by electrolysis and a mixture of the two gases was stored for use as a fuel. La Cour was the first to discover that fast rotating wind turbines with fewer rotor blades were the most efficient in generating electricity and in 1904 he founded the Society of Wind Electricians.
Uploaded
July 21st, 2013
Statistics
Viewed 2,325 Times - Last Visitor from New York, NY on 04/21/2024 at 3:57 PM
Embed
Share
Sales Sheet